Improving operational flexibility of decarbonized thermal power plants with energy storage towards increased renewable sources utilization
Green Program of Cooperation between Science and Industry

Background and Motivation
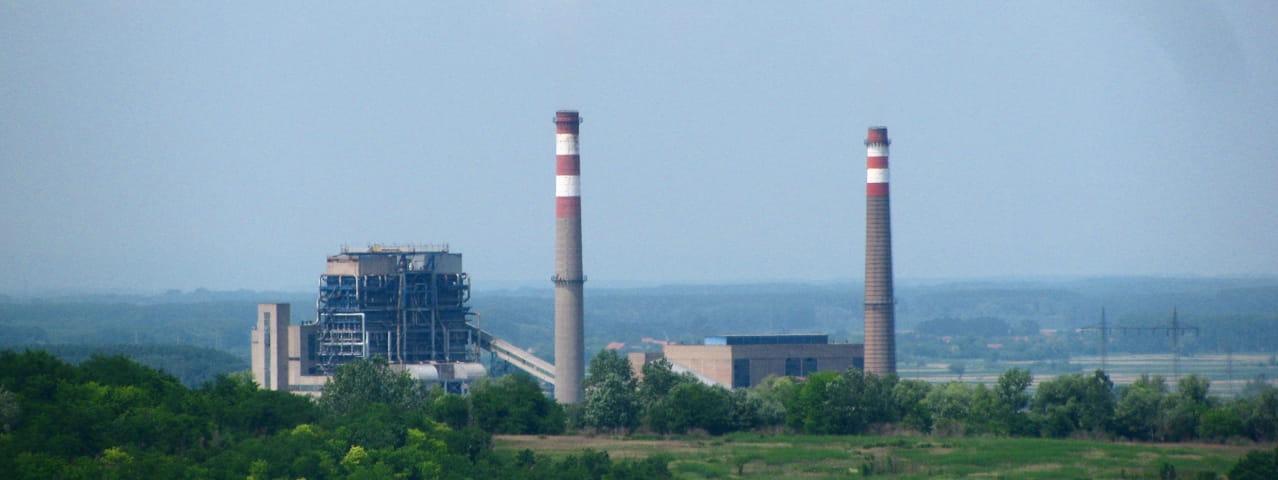
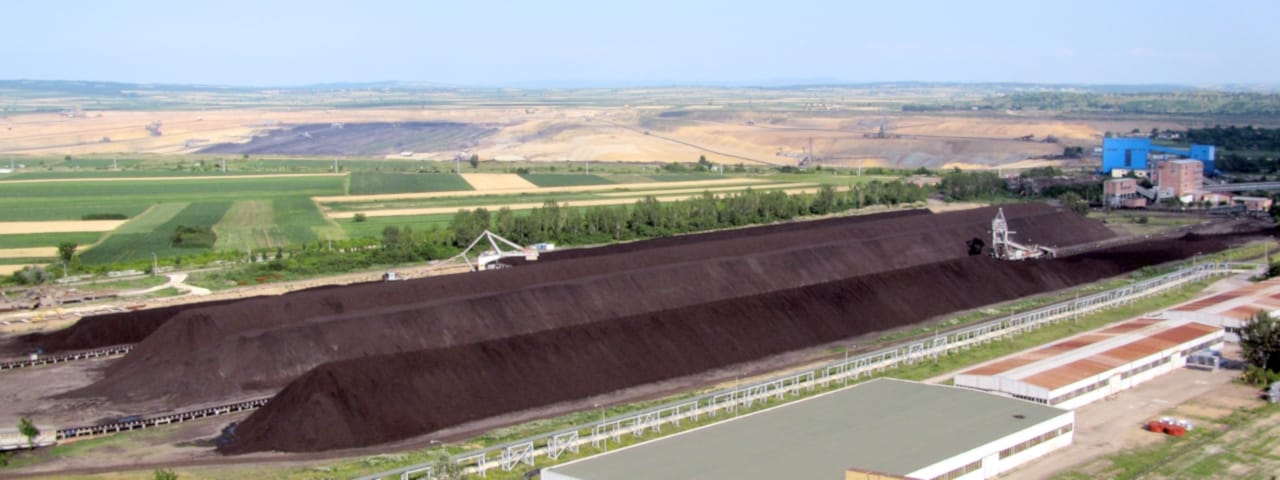
The electricity generation in the Republic of Serbia relies strongly on lignite-fired power plants as presented in figure below - about 70% of total electricity is generated in these plants. Hence, the decarbonization of the thermal power plants is urgent as the Republic of Serbia plans to be in the alliance for the reduction of CO2 emission and mitigation of global warming.
More detailsAmbition
The solutions for energy technology transformations and developments towards decarbonised power generation and increased thermal power plant flexibility to be achieved in TPP-RSU will be a strong support to development plans and outlooks to be defined by governmental bodies, Electric Power Industry and other policy makers and planers tracing the way of green transition towards safe, reliable and economically beneficial electrical energy systems in the Republic of Serbia. The implementation of TPP-RSU project will be of great significance for promoting of the Republic of Serbia as the regional leader in the field of retrofitting of current coal-fired power plants since the countries from the region face similar situation of high share of electricity generated from coal.
More detailsObjectives
The overall research goal of TPP-RSU is development of retrofitted and advanced designs of power plant fleet, which is energy efficient, climate neutral, economically beneficial and operationally safe and reliable. To reach this goal, the following two steps are crucial: (i) decarbonisation of current coal-fired power plants, i.e. substantial or complete elimination of carbon-dioxide (CO2) emission in power generation and (ii) improvement of power plant flexibility.
More detailsResearch focus
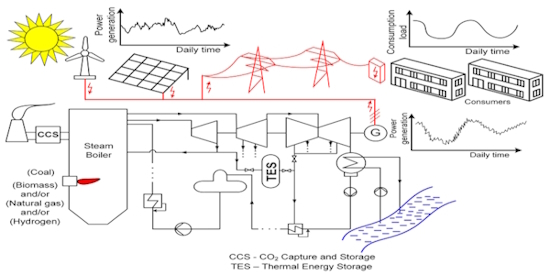
A provision of flexible decarbonized power plant fleet requires assessment of all aspects of their dynamic operational conditions. As example, figure below schematically presents the measures to be undertaken in a coal-fired power plant in order to increase the share of intermittent solar and wind power generation in an electric power system
More detailsInnovation
The proposed solutions for flexibility improvement, maneuvering with distribution of feedwater flow rate distribution and thermal energy storage by implementation of the steam accumulator(s), are novel technical and technological methods and designs. These novel concepts are superior to the current method of control reserve because steam throttling in front of the turbine is avoided. The elimination of the constant energy loss by steam throttling reduces, namely, the energy consumption and consequent negative effects of fuel consumption on the environment. Further, the preliminary analyses show that the proposed thermal energy storage is also superior to other possible methods for power control reserve utilization, such as condensate line flow throttling, variable cooling water flow through turbine plant condenser, feedwater by-pass of high pressure feedwater heaters, due to one or several reasons: greater storage capacity, shorter time of activation, higher power increase, etc.
Project impact
The execution of TPP-RSU would have multiple positive impacts on: Society through implementation of decarbonised energy policy that provides significantly reduced CO2 emission; Electric power utilities through environmentally acceptable and decarbonised electricity generation with competitive prices; Energy and environmental policy makers through well founded and validated data and technological solutions (to be provided in the framework of TPP-RSU) for the transition towards decarbonised power generation; Economy and companies that produce energy equipment and provide energy services through the technological development, manufacturing of new energy equipment and deployment of new energy facilities.
More details